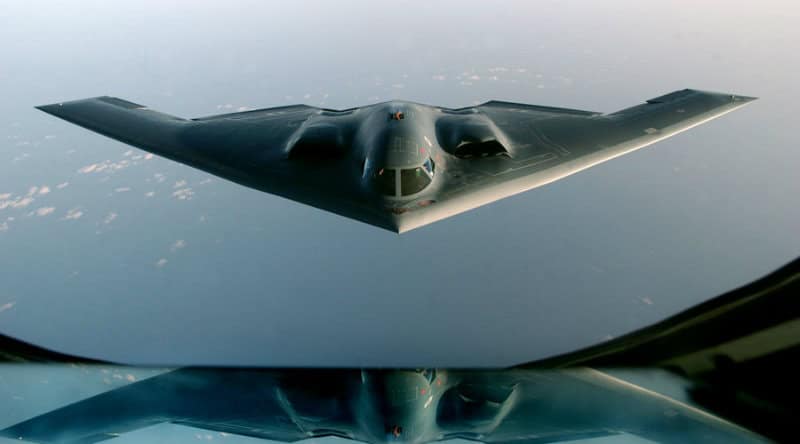
BEIJING – A Chinese firm has claimed to have developed radar technology that can detect stealth jets.
The first Chinese quantum radar was developed by the Intelligent Perception Technology Laboratory of the 14th Institute in CETC, according to Xinhua news agency. CETC stands for Electronics Technology Group Corporation, a defense and electronics firm.
Read: Is India’s first home-built fighter jet better than Pak-China produced JF-17?
The radar is capable of detecting a target at a range of 60 miles and was tested in mid-August, Xinhua said in a report yesterday.
It is believed the radar uses quantum entanglement photons, which means it has better detection capabilities than conventional systems.
This means it can more easily track modern aircraft that use stealth technology or baffle enemy radar.
The new technology also comes after China launched the world’s first quantum communications satellite, which uses quantum entanglement to solve codes.
Read more: China will “get involved” if India tries to disrupt CPEC
Claim of the new radar technology comes after China announced it is considering building a manned radar station on the moon. The facility could include living quarters for astronauts and a powerful radar antenna, stretching at least 164 feet (50 metres) high.
Quantum radar is a device that uses quantum entanglement photons to provide better detection capabilities than conventional radar systems. The method would be useful for tracking targets with a low radar cross section, such as modern aircraft using stealth technology or targets employing active countermeasures to jam or baffle enemy radar.
The technology may also find use in biomedicine, since quantum radar requires lower energy and can be used to non-invasively probe for objects with low reflectivity, such as cancer cells.
The government project was launched earlier this year and a group of scientists received kick-start funding of 16 million yuan (£1.8 million/$2.4 million) from the National Natural Science Foundation of China.