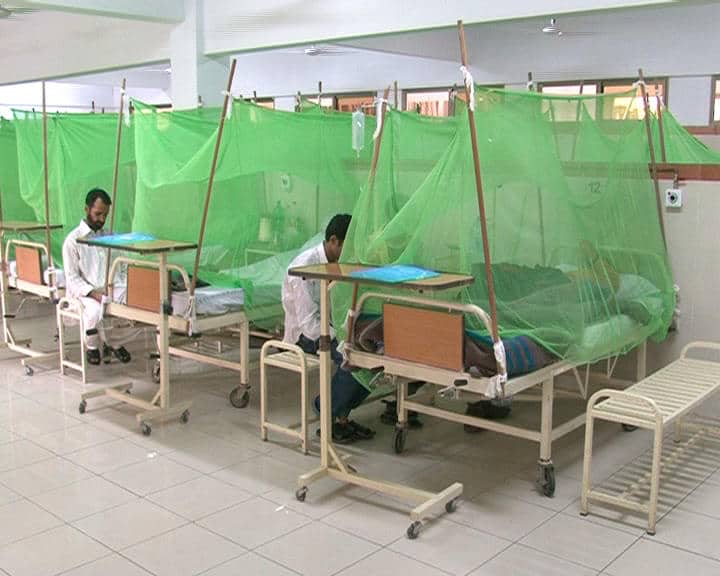
RAWALPINDI – The number of dengue patients has reached 210 in Punjab’s Rawalpindi with cantonment area being affected the most.
A district health official, Dr. Zeeshan said the present weather is suitable for breeding of dengue larvae, with the result that the number of dengue cases is continuously increasing while the district government and Health Authority have made arrangements to control the situation.
To cope with dengue fever spread, 50 entomologists and 20 doctors have been appointed by the deputy commissioner to monitor the anti-dengue activities in Rawalpindi Cantonment Board areas, he added.
He further said that storage of water, and open drains in city and cantonment areas had increased the number of dengue patients in the city.
A full-scale fumigation drive is underway in different localities of the city and cantonment especially where dengue larva has been found, he added.
The authorities advised the residents to take precautionary measures and not panic as dengue fever is curable with timely and proper treatment, adding that the threat of dengue fever spread would end soon as the weather conditions changes.
Key facts
- Dengue is a mosquito-borne viral infection.
- The infection causes flu-like illness and occasionally develops into a potentially lethal complication called severe dengue.
- The global incidence of dengue has grown dramatically in recent decades. About half of the world’s population is now at risk.
- Dengue is found in tropical and sub-tropical climates worldwide, mostly in urban and semi-urban areas.
Severe dengue is a leading cause of serious illness and death among children in some Asian and Latin American countries. - There is no specific treatment for dengue/ severe dengue, but early detection and access to proper medical care lowers fatality rates below 1%.
- Dengue prevention and control depends on effective vector control measures.
Prevention and control
At present, the main method to control or prevent the transmission of dengue virus is to combat vector mosquitoes through:
- Preventing mosquitoes from accessing egg-laying habitats by environmental management and modification.
- Disposing of solid waste properly and removing artificial man-made habitats;
covering, emptying and cleaning of domestic water storage containers on a weekly basis. - Applying appropriate insecticides to water storage outdoor containers.
- Using of personal household protection such as window screens, long-sleeved clothes, insecticide treated materials, coils and vaporizers.
- Improving community participation and mobilization for sustained vector control.
- Applying insecticides as space spraying during outbreaks as one of the emergency vector-control measures.
- Active monitoring and surveillance of vectors should be carried out to determine effectiveness of control interventions.
- Careful clinical detection and management of dengue patients can significantly reduce mortality rates from severe dengue.